Molar mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry that allows us to bridge the gap between the microscopic world of atoms and molecules and the macroscopic world of measurable quantities. It is essential for various chemical calculations, including stoichiometry, solution preparation, and material science. This guide will delve into what molar mass is, how to calculate it accurately, and provide enhanced examples for better understanding.
What is Molar Mass?
Molar mass is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is the SI unit for the amount of substance, and it contains Avogadro’s number of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.), which is approximately 6.022 x 1023.
- Units: Molar mass is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
- Importance: Knowing the molar mass allows you to convert between grams and moles, which is crucial for stoichiometric calculations in chemistry.
Key Concepts:
- Atomic Mass: The mass of a single atom of an element, usually expressed in atomic mass units (amu). On the periodic table, the atomic mass is the weighted average of the masses of an element’s isotopes.
- Molecular Mass (or Formula Mass): The sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a molecule or formula unit. For ionic compounds, it’s referred to as formula mass.
- Avogadro’s Number: 6.022 x 1023 particles per mole. This constant provides a conversion factor between the number of particles and moles.
How to Calculate Molar Mass
Calculating molar mass involves a straightforward process:
- Identify the Chemical Formula: Determine the chemical formula of the substance (e.g., H2O for water, CO2 for carbon dioxide, NaCl for sodium chloride).
- Find Atomic Masses: Look up the atomic mass of each element present in the chemical formula from a reliable periodic table. These values are typically given in amu, but for molar mass calculations, we use them directly in g/mol.
- Sum the Masses: For each element, multiply its atomic mass by the number of times it appears in the chemical formula. Then, sum these products to get the total molar mass of the compound.
Visualizing Molar Mass Calculation
To better understand the concept, consider the visual representation below, which illustrates how individual atomic masses contribute to the overall molar mass of a molecule: (e.g. H2O and CO2)
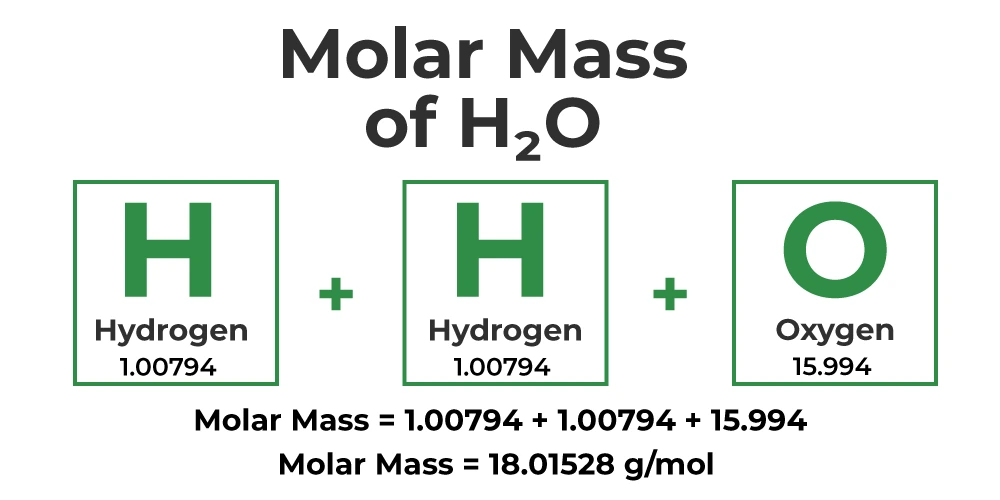
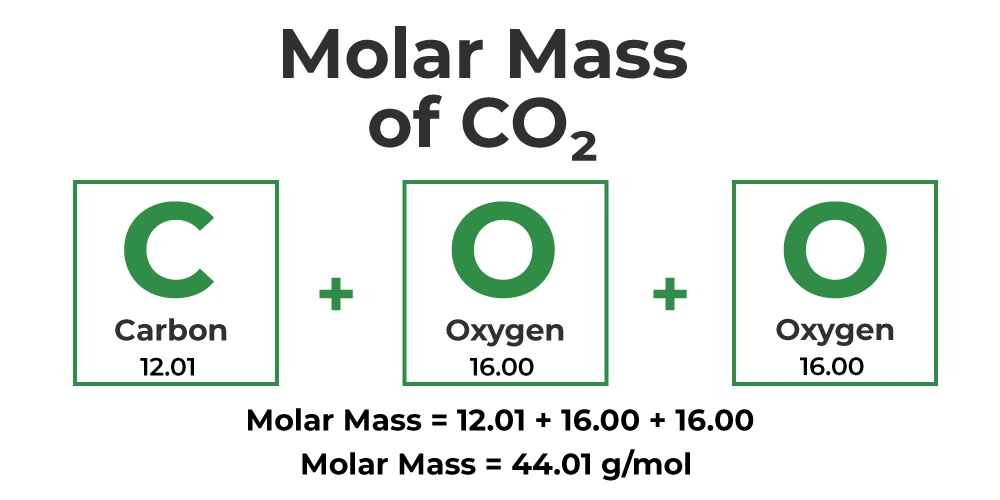
Example Calculations
Let’s walk through some examples with detailed, step-by-step calculations to solidify your understanding. We will use the Python script developed to demonstrate these calculations interactively.
Example 1: Water (H2O)
Chemical Formula: H2O
Atomic Masses:
- Hydrogen (H): 1.008 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 15.999 g/mol
Calculation:
- Hydrogen: 2 atoms × 1.008 g/mol/atom = 2.016 g/mol
- Oxygen: 1 atom × 15.999 g/mol/atom = 15.999 g/mol
Total Molar Mass: 2.016 g/mol + 15.999 g/mol = 18.015 g/mol
Example 2: Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Chemical Formula: CO2
Atomic Masses:
- Carbon (C): 12.011 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 15.999 g/mol
Calculation:
- Carbon: 1 atom × 12.011 g/mol/atom = 12.011 g/mol
- Oxygen: 2 atoms × 15.999 g/mol/atom = 31.998 g/mol
Total Molar Mass: 12.011 g/mol + 31.998 g/mol = 44.009 g/mol
Example 3: Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
Chemical Formula: NaCl
Atomic Masses:
- Sodium (Na): 22.990 g/mol
- Chlorine (Cl): 35.453 g/mol
Calculation:
- Sodium: 1 atom × 22.990 g/mol/atom = 22.990 g/mol
- Chlorine: 1 atom × 35.453 g/mol/atom = 35.453 g/mol
Total Molar Mass: 22.990 g/mol + 35.453 g/mol = 58.443 g/mol
Example 4: Glucose (C6H12O6)
Chemical Formula: C6H12O6
Atomic Masses:
- Carbon (C): 12.011 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 1.008 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 15.999 g/mol
Calculation:
- Carbon: 6 atoms × 12.011 g/mol/atom = 72.066 g/mol
- Hydrogen: 12 atoms × 1.008 g/mol/atom = 12.096 g/mol
- Oxygen: 6 atoms × 15.999 g/mol/atom = 95.994 g/mol
Total Molar Mass: 72.066 g/mol + 12.096 g/mol + 95.994 g/mol = 180.156 g/mol
Practical Applications of Molar Mass
Molar mass is not just a theoretical concept; it has numerous practical applications in chemistry and related fields:
- Stoichiometry: It is crucial for calculating the amounts of reactants consumed and products formed in chemical reactions.
- Solution Preparation: Chemists use molar mass to determine the precise mass of a solute needed to prepare solutions of specific concentrations.
- Material Science: Understanding molar mass helps in analyzing the composition, purity, and properties of various materials.
- Quantitative Analysis: In analytical chemistry, molar mass is used in techniques like gravimetric analysis and titration to determine the quantity of a substance.
Tips for Accurate Molar Mass Calculation
- Always Use a Reliable Periodic Table: Atomic masses can vary slightly depending on the source. Use a consistent and accurate periodic table for your calculations.
- Pay Attention to Significant Figures: While the examples here use a few decimal places, in real-world applications, consider the significant figures of the atomic masses and apply them correctly to your final answer.
- Practice Regularly: The more you practice calculating molar masses for different compounds, the more proficient and confident you will become.
- If you’d like to skip the manual steps and get results instantly, try our Molecular Weight Calculator to find the molar mass of any compound.
Conclusion
Mastering molar mass calculation is a foundational skill for anyone studying or working in chemistry. It unlocks the ability to perform a wide range of quantitative analyses and understand chemical reactions at a deeper level. By following the steps outlined and practicing with various examples, you will be well-equipped to tackle more complex chemical problems. Happy calculating!
References and Further Reading:
- https://uen.pressbooks.pub/introductorychemistry/chapter/molar-mass/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c_zHROisdP4
- https://conquerchemistry.com/2017/07/26/calculate-molar-mass/
- https://www.albert.io/blog/molar-mass-explanation-and-examples/
- https://sciencenotes.org/molar-mass-and-how-to-find-it/


